Acne
Symptoms of Acne
Acne is a common skin condition that affects most people at some point. It causes spots, oily skin and sometimes skin that's hot or painful to touch.
Acne most commonly develops on the:
- face – this affects almost everyone with acne
- back – this affects more than half of people with acne
- chest – this affects about 15% of people with acne
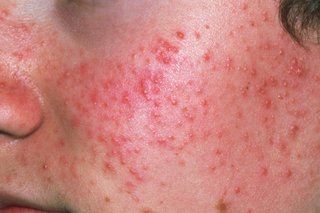
Types of Spots
There are 6 main types of spot caused by acne:
- blackheads – small black or yellowish bumps that develop on the skin; they're not filled with dirt, but are black because the inner lining of the hair follicle produces colour
- whiteheads – have a similar appearance to blackheads, but may be firmer and will not empty when squeezed
- papules – small red bumps that may feel tender or sore
- pustules – similar to papules, but have a white tip in the centre, caused by a build-up of pus
- nodules – large hard lumps that build up beneath the surface of the skin and can be painful
- cysts – the most severe type of spot caused by acne; they're large pus-filled lumps that look similar to boils and carry the greatest risk of causing permanent scarring
Things you can try if you have acne
These self-help techniques may be useful:
- Do not wash affected areas of skin more than twice a day. Frequent washing can irritate the skin and make symptoms worse.
- Wash the affected area with a mild soap or cleanser and lukewarm water. Very hot or cold water can make acne worse.
- Do not try to "clean out" blackheads or squeeze spots. This can make them worse and cause permanent scarring.
- Avoid using too much make-up and cosmetics. Use water-based products that are described as non-comedogenic. This means the product is less likely to block the pores in your skin.
- Completely remove make-up before going to bed.
- If dry skin is a problem, use a fragrance-free water-based emollient.
- Regular exercise cannot improve your acne, but it can boost your mood and improve your self-esteem. Shower as soon as possible once you finish exercising as sweat can irritate your acne.
- Wash your hair regularly and try to avoid letting your hair fall across your face.
Although acne cannot be cured, it can be controlled with treatment.
If you develop mild acne, it's a good idea to speak to a pharmacist for advice.
Several creams, lotions and gels for treating spots are available to buy from pharmacies.
Products containing a low concentration of benzoyl peroxide may be recommended, but be careful as this can bleach clothing.
If your acne is severe or appears on your chest and back, it may need to be treated with antibiotics or stronger creams that are only available on prescription.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If you have mild acne, speak to a pharmacist about medicines to treat it.
If these do not control your acne, or it's making you feel very unhappy, see a GP.
You should see a GP if you have moderate or severe acne or you develop nodules or cysts, as they need to be treated properly to avoid scarring.
Try to resist the temptation to pick or squeeze the spots, as this can lead to permanent scarring.
Treatments can take up to 3 months to work, so do not expect results overnight. Once they do start to work, the results are usually good.
Other possible causes
Acne is known to run in families. If both your mother and father had acne, it's likely that you'll also have acne.
Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during the menstrual cycle or pregnancy, can also lead to episodes of acne in women.
There's no evidence that diet, poor hygiene or sexual activity play a role in acne.
Who's affected?
Acne is very common in teenagers and younger adults. About 95% of people aged 11 to 30 are affected by acne to some extent.
Acne is most common in girls from the ages of 14 to 17, and in boys from the ages of 16 to 19.
Most people have acne on and off for several years before their symptoms start to improve as they get older.
Acne often disappears when a person is in their mid-20s.
In some cases, acne can continue into adult life. About 3% of adults have acne over the age of 35.
When to see a GP
See a GP if your acne is moderate or severe, or medicine from your pharmacy has not worked, as you probably need prescription medicine.
Prescription medicines that can be used to treat acne include:
- topical retinoids
- topical antibiotics
- azelaic acid
- antibiotic tablets
- in women, the combined oral contraceptive pill
If you have severe acne, your GP can refer you to an expert in treating skin conditions (dermatologist).
For example, if you have:
- a large number of papules and pustules on your chest and back, as well as your face
- painful nodules
- scarring, or are at risk of scarring
A combination of antibiotic tablets and topical treatments is usually the first treatment option for severe acne.
Hormonal therapies or the combined oral contraceptive pill can also be effective in women who have acne.
But the progestogen-only pill or contraceptive implant can sometimes make acne worse.
Many of these treatments can take 2 to 3 months before they start to work.
It's important to be patient and persist with a recommended treatment, even if there's no immediate effect.
Page created: 08 October 2019